Factory Activity: China’s manufacturing PMI rises to 50.2 after a two-month contraction, boosted by post-Lunar New Year revival in production.
Factory Activity increased in China’s manufacturing sector, with PMI rising to 50.2 in February.
Lunar New Year holiday resumption and corporate orders boosted production data.
Large companies show significant growth at 52.5, while small enterprises face challenges, remaining at 46.3.
The U.S.-China trade tensions continue with the announcement of higher U.S. tariffs by March 4.
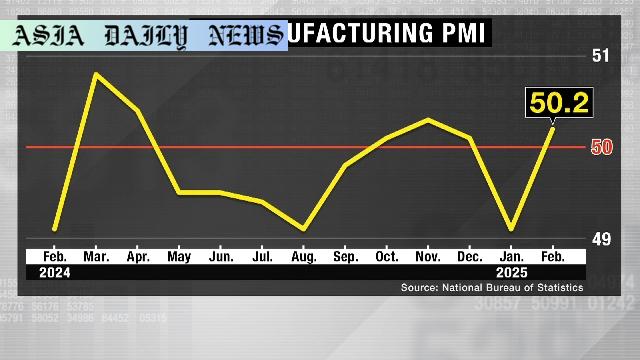
China’s Factory Activity Registers Growth Following Two-Month Contraction
After a troubling two-month contraction, China’s factory activity showcased signs of a rebound in February 2023. The latest data from the National Bureau of Statistics reveals that the country’s manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) climbed to 50.2, up from the previous month’s 49.1. A PMI score above 50 signifies industry growth, and this recovery is attributed to a strategic blend of resumed corporate operations and increased new orders following the Lunar New Year holiday celebrations.
The improvement primarily reflects post-holiday production recovery among large manufacturers, which scored a robust 52.5 on the index. However, challenges persist for other sectors, with midsize enterprises registering a slight contraction at 49.2, and small enterprises struggling at 46.3. Despite these variances, the overall optimism stems from increased domestic demand, which the government has actively encouraged through measures like real estate market revitalization and attempts to revive consumer confidence.
Non-Manufacturing Sector and Broader Economic Indicators
In addition to manufacturing, China’s non-manufacturing PMI, which gauges the service and construction sectors, edged up slightly to 50.4 in February from January’s reading of 50.2. This improvement, though modest, reflects a slowly stabilizing economy. It’s worth noting that the Chinese government has made concerted efforts to bolster the economy, implementing initiatives to stimulate demand and address the real estate downturn.
However, external pressures weigh heavily on the economy. Renewed trade tensions with the United States could strain recovery prospects. U.S. President Donald Trump recently announced plans to double tariffs on Chinese goods from 10 percent to 20 percent, effective March 4. This escalates a trade war that could impact China’s exports and economic growth trajectory significantly.
The Global Impact of U.S.-China Trade Tensions
Beyond national borders, the U.S.-China trade dispute echoes globally. Increased tariffs on Chinese goods could disrupt global supply chains, inflate consumer prices, and potentially curtail multinational investments. For China, higher tariffs might diminish profit margins for exporters, challenge manufacturing growth momentum, and delay recovery in weaker sectors.
Economic analysts are closely monitoring whether Beijing will respond with equal trade restrictions or pursue diplomatic solutions. In the meantime, businesses in both nations remain on edge, strategizing contingencies to mitigate the looming uncertainties.
Going Forward: The Long-Term Forecast
China’s February PMI data presents a glimmer of hope for its manufacturing industry. The government’s targeted initiatives, focusing on key economic drivers like real estate and consumer demand, demonstrate its determination to stabilize growth. However, macroeconomic headwinds from potential escalations in the trade war with the United States serve as stark reminders of the fragility of global economic interconnectedness.
While large enterprises showed significant recovery, the struggles of smaller businesses highlight areas for policymakers to address, ensuring balanced growth. As March approaches, all eyes are on whether China’s government will introduce further relief measures to counter external trade risks and support sectors still grappling with contraction.



Commentary
A Positive Step Forward for China’s Manufacturing Sector
China’s recent PMI data offers a promising glimpse into the nation’s economic resilience. With factory activity climbing back into the growth zone, it demonstrates the intrinsic dynamism of China’s manufacturing powerhouse. The Lunar New Year holidays historically impact production, and the subsequent rebound is a testament to economic revival efforts. The growth, however, is not uniform, and small enterprises continue to lag behind, reflecting an area that policymakers need to address with urgency.
Challenges Looming from U.S.-China Trade Frictions
The specter of heightened U.S. tariffs adds a layer of complexity to China’s recovery. As President Trump intensifies trade measures, the fragile equilibrium achieved within the manufacturing sector risks being destabilized. Tariffs might dampen demand for Chinese exports, though they also offer an opportunity for China to reinforce its domestic-market focus.
A Balancing Act: Stimulating Growth amid Global Pressures
Navigating economic recovery amid global constraints is no small feat. Beijing’s proactive measures, including attempts to revive real estate and spur domestic spending, are vital steps. However, sustaining this growth will likely require additional policies and incentives tailored to support smaller businesses and offset export vulnerabilities.
Conclusion: The Path Ahead
While China’s February PMI figure injects much-needed optimism into discussions of its economic future, the road ahead is far from easy. Global economic interdependence underlines both opportunities and risks, reminding us that a fine balance is essential for sustainable growth. As trade tensions with the United States evolve, businesses and policymakers alike are bracing for potential challenges, keenly aware of the stakes at hand for economic stability worldwide.