Whooping Cough: Cases of whooping cough in Japan hit a record high for the third consecutive week with serious health concerns.
- Whooping cough cases in Japan hit 7,084 in 2023, surpassing last year’s total by 3,000.
- The disease poses fatal risks for infants up to six months old.
- Japan Pediatric Society urges immediate vaccination for infants at two months of age.
- Drug-resistant strains complicate treatment and raise health concerns.
- Medical institutions reported 1,222 cases in the week leading to April 13.
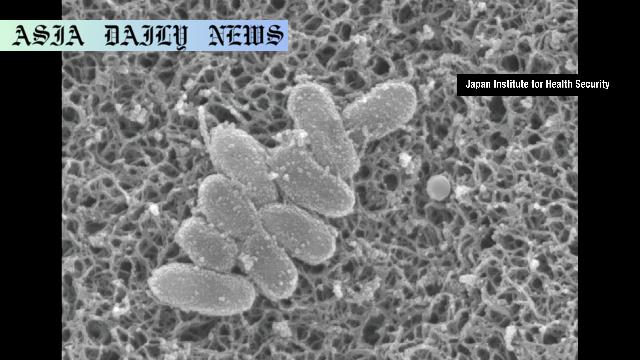
Introduction to the Alarming Surge
Japan is grappling with a record surge in whooping cough cases, marking a significant public health challenge. For the third week in a row, cases of the infectious disease have reached historic highs, bringing the total number of infections for 2023 to 7,084 by mid-April. Alarmingly, this is already a drastic increase of 3,000 cases compared to last year. The rapid spread of this respiratory illness, coupled with fatalities and complications caused by drug-resistant strains, has amplified concerns among healthcare professionals and policymakers. This article delves into the nuances of this public health crisis, its implications, and the vital steps needed to mitigate its impact.
Understanding Whooping Cough and Its Impact
Whooping cough, or pertussis, is a highly infectious bacterial disease that primarily targets the respiratory system. It is caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. The illness is distinguished by severe and persistent coughing fits that can lead to significant respiratory distress. While it affects individuals across all age groups, it poses the gravest danger to infants under six months of age, for whom it can be fatal. In Japan, there have been tragic reports of infant fatalities and cases of severe illness due to this outbreak. As the disease spreads, the medical community emphasizes the urgency of preventive measures such as vaccinations and public awareness campaigns.
Statistical Insights
Medical records indicate a staggering rise in whooping cough infections. In the week ending April 13, 2023, Japan’s medical institutions reported 1,222 new cases—an increase of 500 cases from the prior week. This marked the highest weekly figure since Japanese health authorities began their current record-keeping method in 2018. Overall, this year’s reported cases have already outpaced last year’s total by mid-April. The exponential rise in cases serves as a grim reminder of the disease’s infectious nature and underscores the need for robust and immediate action.
Contributing Factors and Challenges
A concerning development in this outbreak is the emergence of drug-resistant strains of Bordetella pertussis. These strains complicate treatment protocols and limit the effectiveness of conventional antibiotics, posing additional hurdles for healthcare providers. Compounding the situation is the relatively low rate of timely vaccination. Despite the availability of vaccines, many parents delay or skip vaccinations for their infants, leaving a vulnerable population unprotected. Public health officials attribute some of the rise in cases to this issue and emphasize education and awareness campaigns to counter misinformation about vaccine safety.
The Call for Vaccination
To combat the surge, the Japan Pediatric Society has issued an urgent call for parents to vaccinate their infants as soon as they turn two months old. Vaccination remains the most effective measure in preventing the spread of this disease, particularly among high-risk groups such as infants and the elderly. The vaccination schedule for pertussis involves multiple doses, starting at two months and continuing through childhood. In addition to protecting the vaccinated individual, immunization contributes to community-level immunity, reducing the disease’s transmission rate.
Broader Public Health Implications
The record cases of whooping cough in Japan highlight broader systemic issues in public health, including the need for more effective outbreak monitoring and response strategies. The medical system must also focus on combating the spread of misinformation about vaccines, which has grown in recent years and may contribute to declining vaccination rates. Moreover, the appearance of drug-resistant strains underscores the importance of continued investment in medical research and the development of more effective antibiotics. Policymakers and public health officials must work in tandem to address these challenges comprehensively.
Conclusion: The Way Forward
Japan’s unprecedented whooping cough outbreak is a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities in public health systems. Immediate and coordinated action is needed to contain the disease and prevent further tragedies. Vaccination campaigns, public education initiatives, and scientific research should be at the forefront of the response. By prioritizing these measures, Japan can mitigate the impacts of this outbreak and set a precedent for managing infectious diseases in the future.



Commentary
The Urgent Need for Public Health Action
The surge in whooping cough cases in Japan is more than just a statistical anomaly—it is a public health crisis requiring immediate and decisive action. The rate at which infections have risen is alarming, and it underscores the critical importance of vaccination in preventing the spread of this highly contagious disease. As a global society, we often take vaccines for granted, forgetting that they represent one of the greatest achievements in modern medicine. This crisis should serve as a wake-up call for parents, healthcare providers, and policymakers alike.
The Role of Vaccination and Public Education
In addressing this crisis, vaccination stands as the most potent tool at our disposal. Yet, vaccine hesitancy fueled by misinformation remains a significant barrier in many parts of the world, including Japan. Parents must recognize that timely vaccination not only protects their children but also contributes to the broader community’s safety by reducing the chain of transmission. Public education campaigns are essential in dispelling myths and emphasizing the safety and efficacy of vaccines. Governments, healthcare providers, and influencers must work collectively to ensure that accurate information reaches every corner of society.
The Broader Implications and Lessons
This outbreak has broader implications for global health policy. The emergence of drug-resistant strains of whooping cough bacteria highlights the urgent need for continued investment in research and development of advanced treatments. It also serves as a reminder of the importance of international cooperation in tackling infectious diseases. As we navigate this crisis, the lessons learned in Japan can inform strategies in other countries facing similar challenges. It is a stark reminder that public health knows no borders, and collective action is essential in safeguarding global health.
A Call to Action
The current outbreak of whooping cough in Japan demands more than just immediate action—it requires a long-term vision for strengthening the healthcare system. From enhancing disease surveillance to promoting public trust in vaccines, every stakeholder has a role to play. Let this crisis not only be a moment of reflection but also a catalyst for meaningful change that ensures the health and safety of future generations.