China’s GDP growth slowed despite strong EV sales and robust factory output in January-March, facing challenges from US trade tariffs.
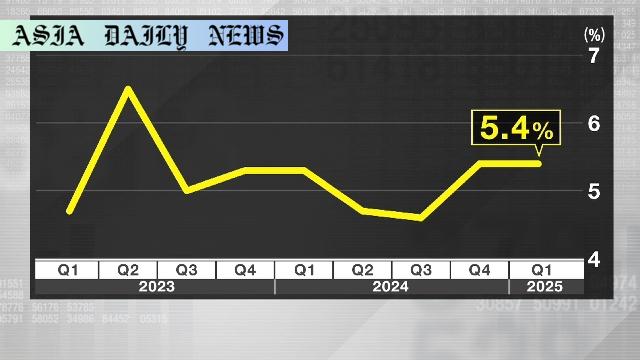
China’s GDP growth stood at 5.4% in Q1 despite trade tensions.
Electric vehicle sales and factory output were key contributors.
US-China tariffs raise concerns about future economic outlook.
Analysis of China’s Q1 GDP Growth
China’s economy demonstrated resilience in the first quarter of this year, posting a growth rate of 5.4% from the same period a year earlier. Despite surpassing the government’s 5% annual target, the growth remained flat compared to the previous quarter. This data, released by the National Bureau of Statistics, reflects both China’s strengths and vulnerabilities in its economic framework.One driver of growth was the thriving sales of electric vehicles (EVs), bolstered by government incentives for green car trade-ins. The emphasis on green energy not only boosts the EV market but positions China competitively in global sustainability efforts. Additionally, factory outputs were robust as exporters rushed to ship goods ahead of US-imposed tariffs, underlining the challenges and opportunities in external trade relations.
Impact of Trade Tensions Between China and the US
However, challenges persist. The ongoing trade standoff between the world’s largest economies has clouded China’s economic horizon. The US recently raised tariffs on Chinese goods to 145%, to which China responded with levies of 125% on US imports. These tit-for-tat tariffs could curtail China’s export-led economy by as much as 3%, affecting long-term economic stability. The economic decoupling exacerbates uncertainties for global supply chains and investors.Domestic Challenges and Consumer Behavior
Domestic factors added to the complexity, as property investment slowed and consumer spending remained stagnant. Chinese consumers, wary of economic uncertainties, are hesitant to spend, contrasting with the otherwise buoyant manufacturing sector. This reluctance hints at deeper structural issues within the economy that might affect future GDP growth. Balancing domestic reform and external trade policies appears crucial for sustainable development.Outlook Moving Forward
Despite these hurdles, China’s commitment to economic stability remains evident. Policymakers may need to strengthen stimulus measures, enhance consumer confidence, and optimize trade strategies to maintain momentum. A renewed focus on driving domestic consumption and strategic engagement in global trade might buffer against external turmoil.Commentary
The Strength and Challenges of China’s Economic Growth
The recent economic data from China signals both progress and caution for the world’s second-largest economy. The 5.4% GDP growth in the first quarter illustrates resilience but also reflects the constraints imposed by both global headwinds and internal dynamics. This duality is emblematic of China’s balancing act between its role as a manufacturing powerhouse and its ambitions for domestic consumer-driven growth.Impact of Trade Policies
The persisting trade dispute with the US undoubtedly presents a significant obstacle. As tariffs escalate, tensions not only disrupt cross-border trade but also challenge the broader economic stability in Asia and beyond. These trade frictions may seem confined in bilateral terms, but their ripple effect across global markets cannot be underestimated. The sharp levies imposed by both nations pose risks that demand strategic reconsideration by policymakers to mitigate impacts.The Way Forward for China
Despite external pressures, China possesses the tools to navigate these turbulent waters. Doubling down on emerging industries, particularly sustainable technologies like electric vehicles, could cement its leadership position. Simultaneously, addressing stagnant domestic demand and strengthening internal policies might stimulate consumption. Global players will closely watch China’s steps in the coming quarters, as its trajectory affects both regional and global economic climates.
Add A Comment


