Whooping Cough: Weekly cases in Japan soar to 3,578, posing risks for infants, especially under six months old.
Surge in Whooping Cough Cases in Japan
In an alarming trend, Japan is witnessing an unprecedented surge in whooping cough cases as weekly figures hit a record high for the third consecutive week. As of the week ending July 6, the number of whooping cough cases reported from medical institutions across the nation reached an extraordinary 3,578. This figure represents a 225-case increase from the prior week, marking the highest numbers since current data collection methods began in 2018. The spike has raised red flags among healthcare authorities, especially as this bacterial infection poses significant risks to vulnerable groups, including infants and young children.
Tokyo leads the case count at 277 reports, followed by Saitama, Gunma, and Kanagawa, each with alarming tallies. By mid-year, the cumulative number of cases has reached 43,728—a stern reminder of the enduring threat posed by this infectious respiratory disease. Experts emphasize its potential for severe complications, particularly among infants younger than six months, where fatalities have been reported this season. Four infants under four months old have already succumbed to the disease by the end of June in Tokyo and select prefectures, highlighting the urgency for preventive measures.
Understanding the Risks and Call for Immediate Actions
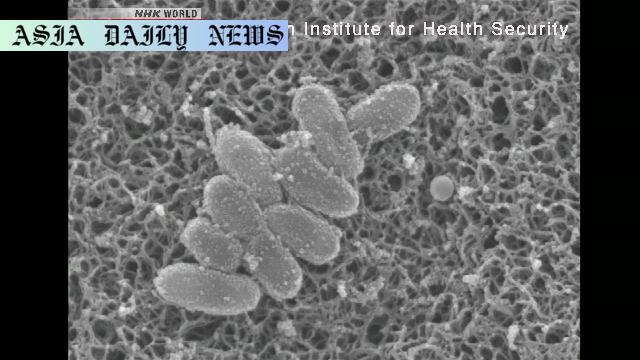
Whooping cough, or pertussis, manifests as severe, persistent coughing that can disrupt normal breathing. Recognized as highly contagious, it is transmitted through respiratory droplets and can lead to severe health complications, including pneumonia, seizures, and in extreme cases, death. The bacterial infection is particularly life-threatening for unvaccinated infants, given their immature immune systems. With resistant strains being reported in hospitals, the need for effective containment strategies becomes even more critical, as conventional medications may not suffice in combating these emerging pathogens.
Addressing the situation, the Japan Pediatric Society has issued an urgent appeal for all parents to ensure their infants are vaccinated promptly once they reach the age of two months. Vaccination remains the most effective preventive measure, helping to curb the transmission rate and protect the most vulnerable population segments. The organization also calls for enhanced awareness campaigns, emphasizing the importance of timely immunization for both children and caregivers.
Tackling the Challenges of Drug Resistance
A worrying development in this crisis is the growing prevalence of drug-resistant strains of Bordetella pertussis, the bacterium causing whooping cough. Reports from medical institutions across various regions suggest that traditional treatment pathways might not be adequate for all cases, complicating healthcare responses. This evolving threat underscores the need for continued research and the development of updated treatment protocols to manage such infections effectively.
In response to the surge in cases and drug resistance concerns, health authorities in Japan are exploring the need for tactical interventions. These include improved diagnostic capabilities for early identification of resistant strains and tailored treatment regimens for affected patients. Collaboration between public health entities, medical professionals, and research institutions is pivotal to containing the disease and preventing future outbreaks. Hospitals and clinics nationwide are also advised to enforce strict infection control measures, limiting the spread of resistant strains within healthcare environments.
The Path Forward: Prioritizing Public Health
The current whooping cough crisis in Japan serves as a sobering reminder of the need for vigilance in public health management. Governments, healthcare organizations, and individuals must collectively prioritize disease prevention measures to safeguard communities from infectious threats. Vaccination drives, awareness campaigns, and enhanced medical research can play transformative roles in this process.
Moreover, as global interconnections increase, infectious disease outbreaks in one region can quickly become international concerns. Thus, neighboring countries must stay informed about the developments in Japan and collaborate on best practices to address potential spillover effects. Investments in healthcare infrastructure and global cooperation will be instrumental in combating outbreaks like the current whooping cough surge.
Commentary
Rising Concerns Over Whooping Cough in Japan
The recent surge in whooping cough cases across Japan is deeply concerning, particularly as it risks the lives of infants. The disease, known for its persistent, severe coughing fits, disproportionately affects young children and poses grave dangers for those under six months old. Hearing about the loss of four infants under such circumstances is a stark reminder of how critical prevention and timely vaccination are in combating infectious diseases.
One alarming aspect of this issue is the presence of drug-resistant cases. When the bacteria responsible for an infection become harder to treat with conventional medications, it creates a double-edged sword that compromises the effectiveness of our healthcare systems. Such resistance not only complicates treatment plans but also heightens the risks for vulnerable populations. This makes it imperative for global health organizations to invest in combating antibiotic resistance and ensuring equitable access to advanced treatment protocols.
The Role of Vaccination and Precautionary Measures
Vaccination has once again proven itself as a powerful tool for disease prevention. Seeing national health authorities emphasize the importance of vaccinating children as early as two months old is a clarion call to all parents. It reminds us of the collective responsibility we share in preventing the spread of potentially fatal infections. Initiatives aimed at community outreach, enabling better access to vaccines, and educating caregivers would be paramount in curbing this public health crisis.
Looking ahead, it is crucial for Japan and other nations to adopt a more proactive stance on public health preparedness. By prioritizing early detection methods, investing in research on emerging pathogens, and promoting awareness at the grassroots level, we can build a society that is resilient in the face of infectious diseases. Only through collective effort and responsibility can we hope to mitigate the impact of outbreaks like this one.


