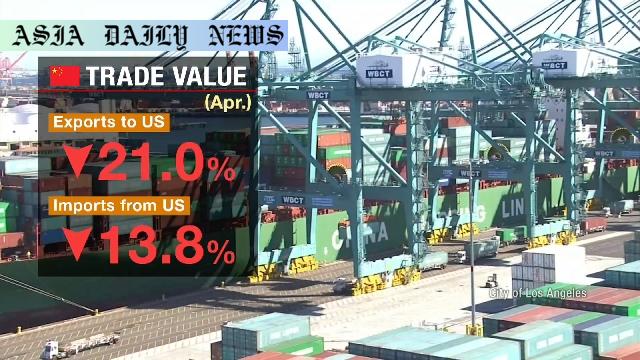
Trade Tensions: China faces a major blow as exports to the United States plummet by 21% in April amidst escalating tariffs.
Escalating Trade Tensions Impact Global Markets
The increasing trade tensions between the two economic superpowers, China and the United States, continue to make waves globally. In April 2023, the escalating situation led to a significant fall in China’s exports to the US, reflecting a 21% decrease compared to the same period last year. Relations between the nations deteriorated months prior, with both sides implementing steep tariffs to curb mutual trade. Notably, Washington imposed a staggering 145% tariff on Chinese goods, while Beijing retaliated with a 125% levy on US imports. This tit-for-tat approach further exasperated economic challenges and caused major disruptions to the flow of goods between the countries.
The Backlash on Bilateral Trade
A 13.8% reduction in imports from the US to China adds to the evidence of the widening trade rift. Businesses on both sides are being squeezed, with many scrambling to adapt to the higher tariffs and rising costs. Historically, China has been a crucial supplier for US businesses, and the disruptions create logistical challenges in addition to inflated import costs. These trends demonstrate how policies aimed at protectionism can lead to broader repercussions not only for the nations involved but also for the wider global economy. As the rift persists, industries reliant on seamless trade between the nations, including technology, manufacturing, and consumer goods, face increasing uncertainty.
Growth in Other Markets Cushions the Blow
Despite the drop in US-bound shipments, China’s overall exports in April showed an 8.1% increase, spurred by booming trade relationships with Southeast Asia and Europe. These developing regions are stepping in to fill the void left by the strained US-China trade, providing a silver lining to China’s export-based economy. Southeast Asia, in particular, has enjoyed a surge in demand for Chinese-made goods. Similarly, a modest rise in trade with Europe further validated China’s global economic adaptability. However, these growing markets likely cannot fully compensate for the lucrative US-China trading partnership many businesses have come to rely upon over decades.
Economic Implications on a Global Scale
The continued divergence of supply chains from China to other nations highlights the new global landscape shaped by trade policies. This reshuffling could lead to a longer-term reorientation of trading ecosystems, with ripple effects visible across different industries. The tariffs imposed by both countries were aimed to force concessions during trade negotiations, but so far, they have deepened economic divides. Analysts worry that ongoing trade restrictions could hurt fragile global economic recovery processes post-pandemic by stoking inflationary pressures, reducing cross-border investments, and fostering a competitive, rather than cooperative, global trade system.
Future Outlook
Efforts to reduce the trade tensions show little progress. Both nations appear committed to their respective stances on tariffs and trade measures. If this situation persists, businesses will likely face persistent challenges determining the best supply chain setups to reduce financial losses. At the same time, middle-income and poor nations reliant on trade with the US and China may suffer from commodity price shocks, as higher tariffs artificially raise overheads in global markets.
Commentary
The Strain of US-China Trade Tensions
The tumultuous trade relationship between the United States and China has entered a new phase of strain, as seen in the sharp drop in their bilateral trade figures in April 2023. This latest chapter of rising tariffs on both sides underscores the complexities of a globalized economy, where the policies of two contributing players can ripple through markets worldwide. For China, the 21% drop in exports to the United States is not just a statistical anomaly but a symptom of deeper economic tensions. Conversely, American businesses and consumers also bear the brunt of higher import costs, which inevitably trickle down to end users in the form of inflated prices.
Ramifications for Global Stakeholders
Beyond affecting trade balances, these dynamics shed light on the vulnerabilities of over-dependence on a single trading partner, be it China for exports or the US for imports. This reliance makes businesses and economies susceptible to policy shifts, essentially forcing them into a precarious balancing act. Moreover, the rising tariffs are symbolic of an ongoing power struggle that extends beyond the realm of economics, touching geopolitical spheres where neither side wants to appear weak.
Room for Optimism?
Despite the challenges, certain developments offer a glimpse of optimism. China’s increase in trade with Southeast Asia and Europe reflects new strategies to diversify its economic ties. It may also inspire businesses globally to reduce dependency on US-China trade altogether. However, policymakers must act in good faith to minimize the long-standing repercussions of trade wars, particularly on smaller nations tethered to global supply chains.
Call for Dialogue
It is imperative for both nations to engage in strategic dialogue and constructive negotiations to de-escalate tensions. Trade wars benefit no one in the long run, and this stalemate exemplifies the importance of collaborative global leadership. Cooperation, not confrontation, will bring about stability that every global citizen ultimately deserves.


